+86 177 5193 6871
222, Block B, Diamond International, Guozhuang Road, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
The steel structure of the multi-functional gymnasium roof of the Third Pavilion of sports Park is a large-span bidirectional orthogonal truss structure, with a width of 145m and a length of 145m, a maximum span of 108m, and a structure standard of 42.5m(see Figure 1). There are altogether 13 trusses (11 main trusses + 2 cantilever trusses), each of which has a mass of 120-180T. The trusses are 9m high, 108m in span, and 42.5m in installation height. They are box section + H-section steel section.
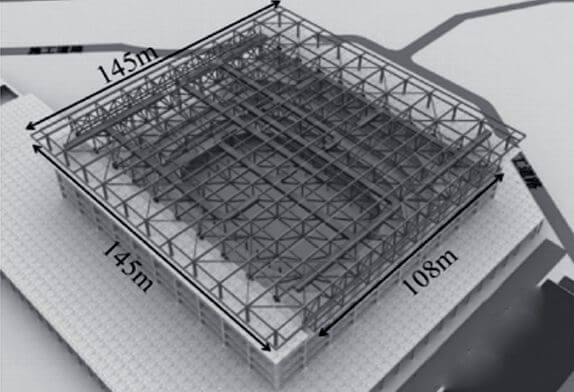
FIG. 1 3d model of steel structure roof
The construction method and process
1.1 Site Layout
Combined with the overall construction deployment of the sports park, based on the construction sequence of the main structure from east to west, the steel component yard, assembly area, crawler crane walking area, and steel structure installation area are set on the site plane (see Figure 2). The main trusses are arranged along the digital axis, from west to east, there are 1 ~ 11 trusses. The east and west sides are cantilever trusses. The 11 trusses are constructed by high altitude cumulative sliding, and the east and west sides cantilever trusses are constructed by high altitude scattered construction. The steel structure assembly area is 120m×15m, and the bulk parts are lifted by an 80T truck crane. The walking area of the crawler crane is 140m×14m, and the installation area of the steel structure is 145m× 145m. A 300T crawler crane is used to lift components to the upper sliding platform and assemble them as sliding units. 8 groups of crawlers are used to provide power for sliding. The frame structure on the north and south sides should be installed and temporarily fixed before sliding construction. A Tower crane and 180T crawler crane should be used to install the outer frame column and frame beam. The steel component yard is 100m×30m to meet the requirement of phased steel component material stacking. The ring road on site is 8m wide and the turning radius is 15m to meet the requirement of steel structure material transferring from the gate to the yard.
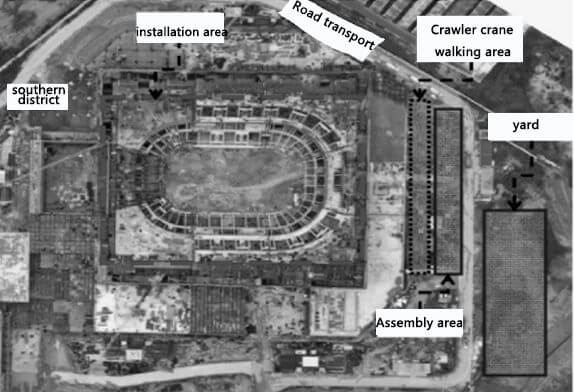
FIG. 2 Construction layout of steel roof
1.2 The truss shall be installed on the whole floor and hoisted in sections. The whole floor assembly adopts the way of horizontal assembling, the truss is placed horizontally on the tire frame, and all sections are overturned and lifted after the assembly and welding are completed. In the assembly process, the structure needs to arch, the maximum arch value is 200mm, and the structure adduction value is 10mm. The truss assembly adopts two – a way arch, and the arch values at both ends decrease successively. The horizontal plying ground should be leveled and compassed, and 300mm thick brick slag should be laid above it.
1.3 The anti-overturning support is set on the sliding track with a section of H250×250×9×14, and the pull-out limit is set between the slipper and the track. Hydraulic synchronous slip adopts a hydraulic tractor, hydraulic pump source system, and computer synchronous control system. Considering the cumulative slip of the element, according to the slip process and the reaction value of the bottom of the support, 8 hydraulic tractors are planned to be arranged when the gym truss slips, and 4, 2, and 2 hydraulic tractors are respectively set for tracks 1 and 2. The horizontal thrust of each hydraulic tractor is 1 000kN, and the total horizontal thrust is 8000kN.

With the development of cities, large-span structures are mostly used in stadiums, airports, stations, and other large public buildings, and the steel truss roof system is increasingly widely used. The cumulative sliding method can effectively solve the unfavorable factors such as narrow site, short construction period, self-weight of components, and difficulty in controlling installation accuracy, and achieve good economic and social benefits.
